There are many options for migrating SQL databases to Azure. With the latest technology you can move just the database and log files, or you can move the entire system. You could move to Azure SQL Database or you could migrate to a VM running SQL Server. The methods that you chose to move will likely depend on what tools you are currently using, your experience with SQL Server and your SQL needs once the database is in Azure. To cover all of this would probably require a 30 part blog post which unfortunately, I do not have the time to write now. In this detailed article we will touch on many of these and provide Step-By-Step guidance for the most popular methods. If you are on the most recent version of SQL Server (2014) there are far more options available to you. Since many may not have that available to them, and migrating from 2014 is so super simple, I will spend most efforts on broader availability solutions. What is super simple you ask…
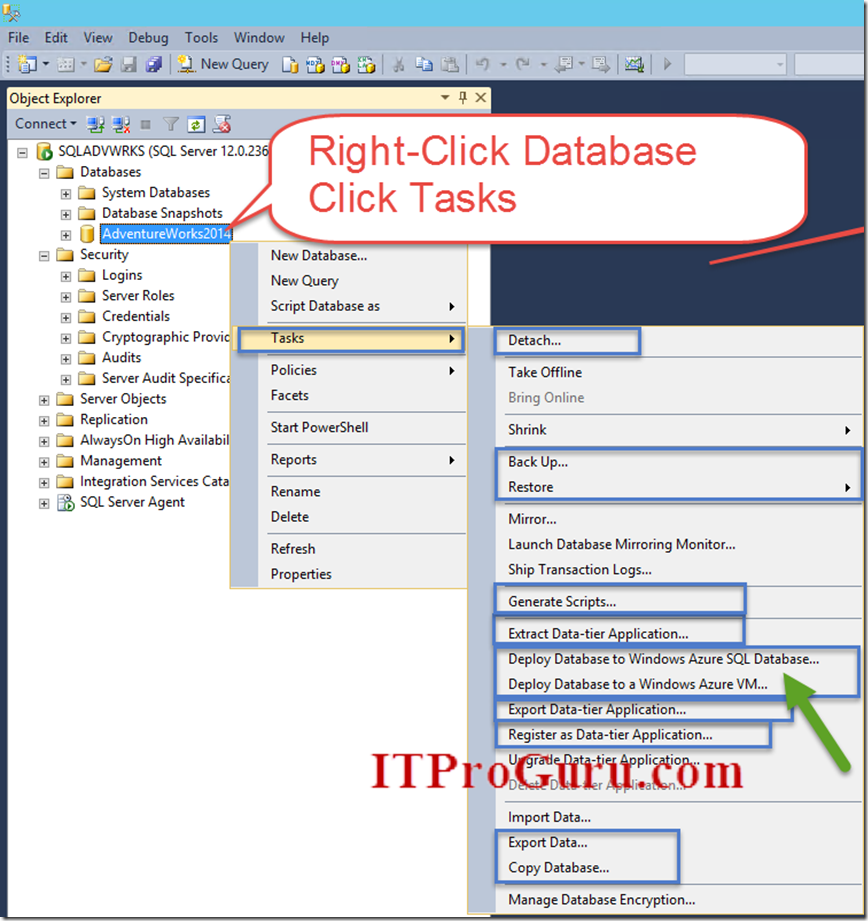
Right-Click on the database you want to move; click Tasks and you have a boat load of options for getting your database moved to Azure. Including “Deploy Database to Windows Azure SQL Database…” or “Deploy Database to a Windows Azure VM…”
Azure SQL Database
First and foremost before determining what the best method is for migrating to Azure consider what functionality you are using or need in SQL Server. Many (dare I say most) databases can be migrated to Azure SQL Database which gives you more application scalability capabilities for much less cost.
Limitations
I would not be serving you well if I did not give you some of the highlights on what gotcha’s you might run into. If you are just using basic features, a small database (less than 2gb for basic, standard and premium, less than 150gb for Web & Business Edition; Exact size and pricing information can be obtained at Pricing Overview) Azure SQL Database may work for you. There are also limitations on use of Transact SQL (example: the USE statement cannot be used to change databases since the databases are not necessarily on the same machine). For more detailed information see Transact-SQL Support (Windows Azure SQL Database), Unsupported Transact-SQL Statements (Azure SQL Database) and Azure SQL Database Transact-SQL Reference. There are other limitations too (example transactional replication, database mirroring and log shipping) see Comparison of SQL Server with Azure SQL Database for a good list of differences. Remember, even if you do want to run SQL in azure but you cannot do it on Azure SQL Database due to limitations, you can run SQL Server in a VM on Azure. See Deploy SQL Server 2014 VM on Azure Cloud for Step-By-Step for creating a SQL server on Windows Azure. Because there are many complications in migrating and upgrading at the same time, I will refer you to Migrating Databases to Azure SQL Database (formerly SQL Azure) & Upgrade to SQL Server 2014 for older versions of SQL and assume you are migrating without upgrading your SQL Database version for the purpose of this article. However, if you want to stay on the same version, you could migrate to SQL Server running on an Azure VM. Azure Virtual Machines has SQL Server 2008 R2 and above in the Virtual Machine Image Gallery. If you need more than that, you could build it on Azure yourself by creating the machine then installing SQL Server yourself. I am not sure of any support or licensing implications of doing this so you may have to do a bit more research.
Migrating Databases to Azure SQL Database (formerly SQL Azure)
You can use the Generate and Publish Scripts Wizard to transfer a database from a local computer to Microsoft Azure SQL Database. The Generate and Publish Scripts Wizard creates Transact-SQL scripts for your local database. The wizard uses them to publish database objects to Microsoft Azure SQL Database. For detailed information on migration, see Migrating SQL Server Databases to Azure SQL Database and Choosing Tools to Migrate a Database to Azure SQL Database in the Migrating Data-Centric Applications to Azure guide.
Migrating Databases to SQL Database by Generating a Script of an Existing Database
To migrate an existing SQL Server database to Azure SQL Database you can export the schema as a Transact-SQL script and then execute that script against Microsoft Azure SQL Database as follows:
- Export a script from SQL Server Management Studio and set the appropriate export options. Because Microsoft Azure SQL Database supports a subset of features found in SQL Server, you may have to make some modifications to the script before you are able to execute it in the cloud.
- Execute the script to create the schema in Microsoft Azure SQL Database.
Step-By-Step
Using the wizard involves the following main steps:
1. Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to an instance of the Database Engine.
2. In Object Explorer, right click a database to open a menu, select Tasks…, and then select Generate Scripts.
3. Choose objects to export.
4. Set scripting options. You have the options to save the script to file, clipboard, new query window; or publish it to a web service.
5. Set advanced scripting options.
By default, the script is generated for stand-alone SQL Server instance. To change the configuration, click the Advanced button from the Set Scripting Options dialog, and then set the Script for the database engine type property to SQL Database.
You can also set the Types of data to script to one of the following based on your requirements: Schema only, Data only, Schema and data.
After the script is created, you have the option to modify the script before running the script against an Azure SQL Database to transfer the database.
Migrating Databases to SQL Database by Using Data-tier Application Export and Import
You can perform a Data-tier Application (DAC) export to migrate both the definition of the objects in a database and the data from the user tables into a DAC export file (BACPAC). You can then copy the BACPAC file into the Azure blob storage service, and perform a DAC import to create a new database containing all of the objects and data. For more information, see How to: Import and Export a Database (Azure SQL Database).
Step-By-Step
What You Need to Know
- Before you begin working with the Import/Export Service, create an Azure storage account for storing BACPAC files. For more information about creating a storage account, see How to Create a Storage Account.
- Use your storage account to create a container for your BACPAC files with a tool like Azure Storage Explorer or the Azure Management Tool (MMC).
- An export operation performs an individual bulk copy of the data from each table in the database, so it does not guarantee the transactional consistency of the data. To make a transactionally consistent copy of a database, use the Azure SQL Database copy database feature to create a transactionally consistent copy of your database, and perform the export of the copy. For more information, see How to: Use Database Copy (Azure SQL Database).
Import a Database into Azure SQL Database
1. Log on to the Azure Platform Management Portal.
2. Click New > Data Services > SQL Database > Import. This will open the Import Database dialog.
3. Navigate to the .bacpac file to import: Click Storage account > Container > BACPAC and then click Open.
4. Specify a name for the new SQL database. The database name must be unique on the server, so you cannot use the name of an existing database, and the name must comply with SQL Server rules for identifiers. For more information, see Identifiers.
5. Specify Subscription, Edition, Max Size, and host Server details. To continue, click the Arrow at the bottom of the dialog.
6. Specify login details for the host server.
7. To start the import operation, click the Check mark at the bottom of the dialog. The portal will display status information in the ribbon at the bottom of the page.
8. To view your new database, click SQL Databases in the navigation pane and refresh the page.
Export a Database from Azure SQL Database
1. Log on to the Azure Platform Management Portal.
2. In the navigation pane, click SQL Databases. In the list view of SQL databases, click the name of the database you would like to export.
3. On the task bar, click Export to open the Export Database dialog.
4. Verify that the database name, Blob Storage Account, destination Container, and host Server information is correct for the SQL database you want to export. Provide the server login details. To continue, click the Check mark at the bottom of the dialog. Note that the server account must be a server-level principal login – created by the provisioning process – or a member of the dbmanager database role.
5. You should see a message saying your export database request succeeded. After the export operation is complete, you can import your BACPAC file into a SQL database server, create a new SQL Server user database in SSMS, or initialize the set of objects in a new data-tier application using SQL Server Data Tools. Before you consider the operation complete and successful, you should verify that the export file can be utilized.
6.
See below…Create a New SQL Database from an Existing Export File
Create a New SQL Database from an Existing Export File
Use the Azure SQL Database Create from Export feature to create a new SQL database from an existing export file.
To create a new SQL database from an existing export file, use the following steps:
Step-By-Step
1. Log on to the Azure Platform Management Portal.
2. In the navigation pane, click All Items> SQL Databases. In the list view of SQL databases, click the name of a database, and then click Configure.
3. Specify a Storage Account, click New Database, and then specify settings for the following parameters:
- Bacpac file name – This is the source file for your new SQL database.
- A name for the new SQL database.
- Server – This is the host server for your new SQL database.
- To start the operation, click the Check mark at the bottom of the page
Migrating Databases to SQL Database by SQL Database Migration Wizard
The SQL Database Migration Wizard walks you through the selection of your SQL objects, creates SQL scripts suitable for Azure SQL Database, and allows you to migrate data between on-premise SQL Server 2005 or 2008 and Azure SQL Database servers, as well as between two or more Azure SQL Databases in the same or different data centers. For more information, see Azure SQL Database Migration Wizard on Codeplex.
Migrating Databases to SQL Database Using Microsoft Sync Framework 2.1
Microsoft Sync Framework 2.1 provides synchronization capabilities between on-premise and Azure SQL Database servers, as well as between two or more Azure SQL Databases in the same or different data centers. Using Sync Framework 2.1, you can extend the schema and data within your SQL Server database or Azure SQL Database to Azure SQL Database data centers around the world to provide geo-available data access. For more information, see Microsoft Sync Framework 2.1 Software Development Kit (SDK). With Sync Framework 2.1, you can extend the reach of your data to the web by leveraging the Windows Azure Platform and SQL Azure Database. By synchronizing a SQL Server database on your business premises to SQL Azure, you make some or all of your data available on the web without the need to provide your customers with a connection to your on premises SQL Server database. After you configure your SQL Azure database for synchronization, users can take the data offline and store it in a client database, such as SQL Server Compact or SQL Server Express, so that your applications operate while disconnected and your customers can stay productive without the need for a reliable network connection. Changes made to data in the field can be synchronized back to the SQL Azure database and ultimately back to the on premises SQL Server database
Migrating Databases to SQL Database by Using Data-tier Application Export and Import
You can perform a Data-tier Application (DAC) export to migrate both the definition of the objects in a database and the data from the user tables into a DAC export file (BACPAC). You can then copy the BACPAC file into the Azure blob storage service, and perform a DAC import to create a new database containing all of the objects and data. For more information, see How to: Import and Export a Database (Azure SQL Database).
Moving Data into SQL Database BCP.exe
Azure SQL Database supports the use of SQL Server Integration Services. SQL Server Integration Services is a convenient way to move data into and out of Azure SQL Database. Alternatively, you can transfer data to Azure SQL Database by using the bulk copy utility (bcp.exe) particularly helpful for older copies of SQL (back to 2000, select “Other Versions” for more options).
SQL Server Integration Services
You can transfer data to Microsoft Azure SQL Database by using SQL Server 2008 Integration Services. In SQL Server 2008 R2 or later, the Import and Export Data Wizard provides support for Azure SQL Database . You can use this tool to migrate on-premise databases to Microsoft Azure SQL Database. For more information, see How to: Run the SQL Server Import and Export Wizard in SQL Server Books Online.
Much More
There are other options as well including the Detach, Move Attach method to move a database file. Now with SQL 2014 you can even move a database from the database tasks dropdown in SQL Server Management Studio and select deploy to Azure. If you wanted to just move the data and log files to Azure storage and keep SQL running locally, you could do that by using the Detach/Attach method. There is PowerShell and other manual copy routines like azCopy to help you get data into Azure. Hopefully this article gives you an option that fits right for you. In the coming months, I will likely be posting much more on Moving SQL to Azure including more Step-By-Step guides with screenshots.